diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index d2d8dc1c..f6c9851e 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ an efficient and convenient toolkit to develop dual-driven ABL systems,
which leverage the power of both data and knowledge.
- +
+
## Installation
diff --git a/docs/Intro/Basics.rst b/docs/Intro/Basics.rst
index c898b03b..39219954 100644
--- a/docs/Intro/Basics.rst
+++ b/docs/Intro/Basics.rst
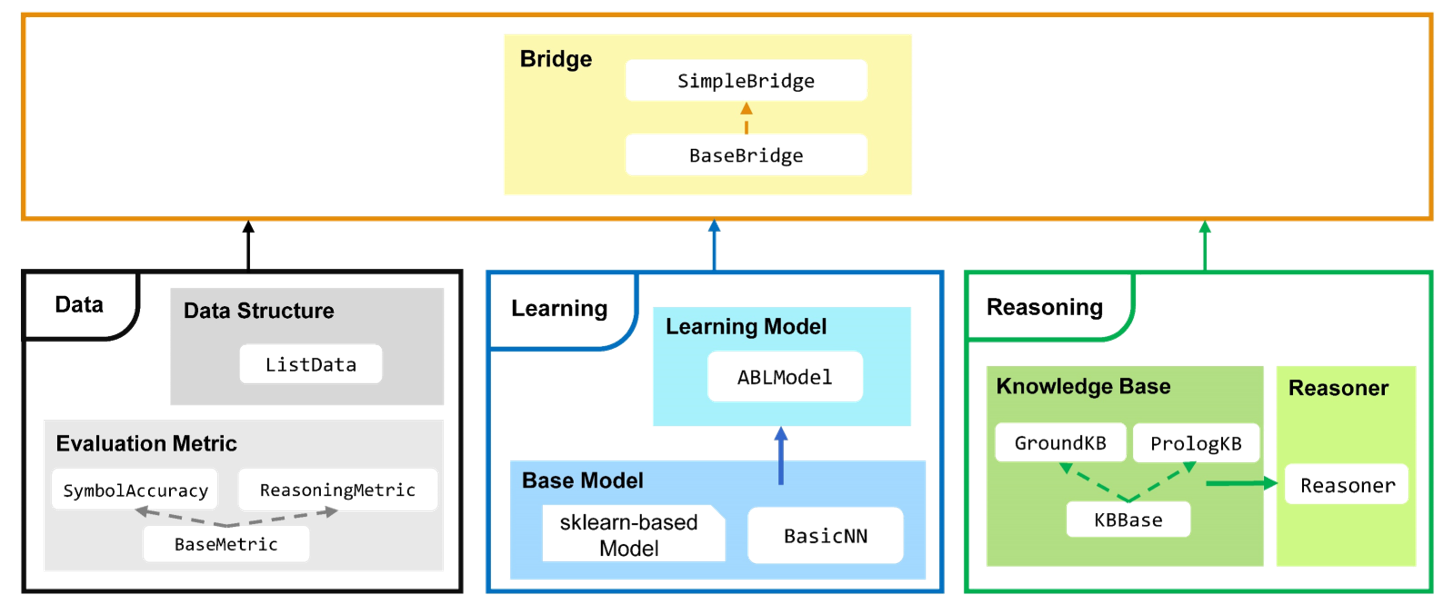
@@ -20,29 +20,28 @@ AI: data, models, and knowledge. Below is an overview of the ABLkit.
.. image:: ../_static/img/ABLkit.png
-**Data** part manages the storage, operation, and evaluation of data efficiently.
+**Data** part efficiently manages data storage, operations, and evaluations.
It includes the ``ListData`` class, which defines the data structures used in
-ABL, and comprises common data operations like insertion, deletion,
+ABLkit, and comprises common data operations like insertion, deletion,
retrieval, slicing, etc. Additionally, it contains a series of evaluation metrics
such as ``SymbolAccuracy`` and ``ReasoningMetric`` (both specialized metrics
-inherited from the ``BaseMetric`` class), for evaluating model quality from a
+inherited from the ``BaseMetric`` class), for evaluating performance from a
data perspective.
:blue-bold:`Learning` part focuses on the construction, training, and
prediction of machine learning models. The ``ABLModel`` class is the
central class that encapsulates the machine learning model. This class is
-compatible with various frameworks, including those based on Scikit-learn
+compatible with various frameworks, including those based on scikit-learn
or PyTorch neural networks constructed by the ``BasicNN`` class.
:green-bold:`Reasoning` part concentrates on constructing domain knowledge and
-performing reasoning. The ``KBBase`` class allows users to define a
+performing reasoning. The ``KBBase`` class allows users to customize a
domain knowledge base. For diverse types of knowledge, we also offer
implementations like ``GroundKB`` and ``PrologKB`` (both inherited
-from the ``KBBase`` class). The latter, for instance, enables
-knowledge bases to be imported in the form of Prolog files.
-Upon building the knowledge base, the ``Reasoner`` class is
-responsible for minimizing the inconsistency between the knowledge base
-and data.
+from the ``KBBase`` class). The latter, for instance, imports
+knowledge bases via Prolog files. Upon building the knowledge base,
+the ``Reasoner`` class is responsible for minimizing the inconsistency
+between the knowledge base and data.
The integration of these three parts is achieved through the
:yellow-bold:`Bridge` part, which features the ``SimpleBridge`` class (derived
diff --git a/docs/Intro/Reasoning.rst b/docs/Intro/Reasoning.rst
index 9a071f84..33ce1631 100644
--- a/docs/Intro/Reasoning.rst
+++ b/docs/Intro/Reasoning.rst
@@ -36,8 +36,8 @@ Building a knowledge base from ``KBBase``
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
For the user-built KB from ``KBBase`` (a derived subclass), it's only
-required to pass the ``pseudo_label_list`` parameter in the ``__init__`` function
-and override the ``logic_forward`` function:
+required to pass the ``pseudo_label_list`` parameter in the ``__init__`` method
+and override the ``logic_forward`` method:
- ``pseudo_label_list`` is the list of possible pseudo-labels (also,
the output of the machine learning model).
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ and override the ``logic_forward`` function:
.. note::
- Generally, the overridden function ``logic_forward`` provided by the user accepts
+ Generally, the overridden method ``logic_forward`` provided by the user accepts
only one parameter, ``pseudo_label`` (pseudo-labels of an example). However, for certain
scenarios, deductive reasoning in the knowledge base may necessitate information
from the input. In these scenarios, ``logic_forward`` can also accept two parameters:
@@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ Out:
Other optional parameters
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-We can also pass the following parameters in the ``__init__`` function when building our
+We can also pass the following parameters in the ``__init__`` method when building our
knowledge base:
- ``max_err`` (float, optional), specifying the upper tolerance limit
@@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ When aiming to leverage knowledge base from an external Prolog file
(which contains how to perform reasoning), we can directly create an
instance of class ``PrologKB``. Upon instantiation of
``PrologKB``, we are required to pass the ``pseudo_label_list`` (same as ``KBBase``)
-and ``pl_file`` (the Prolog file) in the ``__init__`` function.
+and ``pl_file`` (the Prolog file) in the ``__init__`` method.
.. admonition:: What is a Prolog file?
@@ -176,10 +176,10 @@ knowledge base. In this way, the knowledge built will have a Ground KB
accelerate abductive reasoning.
``GroundKB`` is a subclass of ``GKBBase``. Similar to ``KBBase``, we
-are required to pass the ``pseudo_label_list`` parameter in the ``__init__`` function and
-override the ``logic_forward`` function, and are allowed to pass other
+are required to pass the ``pseudo_label_list`` parameter in the ``__init__`` method and
+override the ``logic_forward`` method, and are allowed to pass other
:ref:`optional parameters `. Additionally, we are required pass the
-``GKB_len_list`` parameter in the ``__init__`` function.
+``GKB_len_list`` parameter in the ``__init__`` method.
- ``GKB_len_list`` is the list of possible lengths for pseudo-labels of an example.
 +
+
 +
+