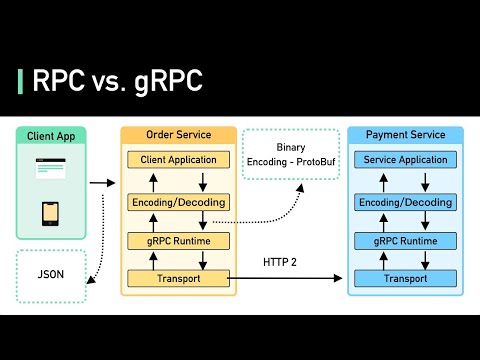
gRPC (gRPC Remote Procedure Call) is a high-performance, open-source framework developed by Google for building scalable and efficient APIs. It uses HTTP/2 for transport, Protocol Buffers (protobuf) as the interface description language, and provides features such as authentication, load balancing, and more.
Protocol Buffers (protobuf) is a language-neutral, platform-neutral, extensible mechanism for serializing structured data. It allows defining data structures in .proto files and generates code in various languages for data serialization and deserialization.
-
Define a .proto file
syntax = "proto3"; package example; // Define the message structure message ExampleMessage { int32 id = 1; string name = 2; bool is_active = 3; } // Define the service service ExampleService { rpc GetExample (ExampleRequest) returns (ExampleResponse); } // Define request and response messages message ExampleRequest { int32 id = 1; } message ExampleResponse { ExampleMessage example = 1; }
-
Data Types
- double, float
- int32, int64, uint32, uint64, sint32, sint64, fixed32, fixed64, sfixed32, sfixed64
- bool
- string
- bytes
-
Field Rules
-
Optional: Fields are optional by default in proto3.
-
Repeated: Represents a list of values.
repeated string tags = 4;
- Reserved Keywords
-
Reserved field numbers and names to prevent future conflicts.
message Sample { reserved 4, 5, 6; reserved "foo", "bar"; }
-
Unary RPC
-
A single request is sent from the client to the server and a single response is returned.
rpc GetExample (ExampleRequest) returns (ExampleResponse);
-
-
Server Streaming RPC
-
The client sends a single request to the server and receives a stream of responses.
rpc GetExampleStream (ExampleRequest) returns (stream ExampleResponse);
-
-
*Client Streaming RPC
-
The client sends a stream of requests to the server and receives a single response.
rpc SendExampleStream (stream ExampleRequest) returns (ExampleResponse);
-
-
Bidirectional Streaming RPC
-
Both client and server send a stream of messages to each other.
rpc ExampleChat (stream ExampleRequest) returns (stream ExampleResponse);
-
For enabling gRPC in web applications, using a proxy like Envoy is recommended. Here is a basic setup:
- Envoy Installation
- Follow the installation instructions from the Envoy documentation.
- Proxy Configuration
-
Save the following configuration in a file named envoy.yaml and run Envoy with this configuration.
static_resources: listeners: - address: socket_address: address: 0.0.0.0 port_value: 8080 filter_chains: - filters: - name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager config: codec_type: AUTO stat_prefix: ingress_http route_config: name: local_route virtual_hosts: - name: backend domains: ["*"] routes: - match: prefix: "/" route: cluster: example_service http_filters: - name: envoy.filters.http.router clusters: - name: example_service connect_timeout: 0.25s type: LOGICAL_DNS lb_policy: ROUND_ROBIN http2_protocol_options: {} load_assignment: cluster_name: example_service endpoints: - lb_endpoints: - endpoint: address: socket_address: address: 127.0.0.1 port_value: 50051
-
Running Envoy
envoy -c envoy.yaml
This will proxy HTTP/1.1 gRPC-Web requests to your gRPC server.
-
Define the service in .proto file
service ExampleService { rpc GetExample (ExampleRequest) returns (ExampleResponse); }
-
Generate gRPC code
-
Use the protoc compiler to generate gRPC code from the .proto file.
protoc --dart_out=grpc:lib/src/generated -Iprotos protos/example.proto
- Setup
-
Add dependencies to pubspec.yaml
dependencies: grpc: ^3.0.0 protobuf: ^2.0.0
-
Generate Dart code from .proto file
protoc --dart_out=grpc:lib/src/generated -Iprotos protos/example.proto
-
Server Implementation
import 'dart:async'; import 'package:grpc/grpc.dart'; import 'package:your_project/src/generated/example.pbgrpc.dart'; class ExampleService extends ExampleServiceBase { @override Future<ExampleResponse> getExample(ServiceCall call, ExampleRequest request) async { // Create a response final example = ExampleMessage() ..id = request.id ..name = 'Example Name' ..isActive = true; return ExampleResponse()..example = example; } } Future<void> main(List<String> args) async { final server = Server([ExampleService()]); await server.serve(port: 50051); print('Server listening on port ${server.port}...'); }
-
Client Implementation
import 'package:grpc/grpc.dart'; import 'package:your_project/src/generated/example.pbgrpc.dart'; Future<void> main(List<String> args) async { final channel = ClientChannel( 'localhost', port: 50051, options: const ChannelOptions(credentials: ChannelCredentials.insecure()), ); final stub = ExampleServiceClient(channel); try { final request = ExampleRequest()..id = 1; final response = await stub.getExample(request); print('Example: ${response.example.name}'); } catch (e) { print('Caught error: $e'); } await channel.shutdown(); }
For more detailed information and advanced usage, refer to the following resources:
- gRPC Official Documentation
- Protocol Buffers Official Documentation
- gRPC-Web Documentation
- Dart gRPC Guide
-
protocCommand Not Found- Ensure that Protocol Buffers compiler (
protoc) is installed and added to your PATH. - Installation instructions can be found here.
- Ensure that Protocol Buffers compiler (
-
gRPC Server Not Starting
- Check if the port (e.g., 50051) is already in use.
- Ensure that all necessary dependencies are added in
pubspec.yamland runpub getto install them.
-
Connection Refused Error
- Ensure the gRPC server is running and accessible at the specified address and port.
- Check network settings and firewall rules.
-
Code Generation Issues
- Verify the syntax and structure of your
.protofiles. - Make sure the
protoccommand is correctly specified, with paths adjusted to your project structure.
- Verify the syntax and structure of your
gRPC supports various authentication mechanisms, including:
- SSL/TLS: For secure communication.
- Token-based Authentication: Using JWT or other tokens.
- OAuth: Integration with OAuth for secure authentication.
gRPC provides built-in support for load balancing, which can be configured in the client.
gRPC uses status codes to indicate the outcome of an RPC call. These status codes are part of the grpc library in Dart and can be handled using try-catch blocks in your client or server code.
```dart
try {
final response = await stub.getExample(request);
print('Example: ${response.example.name}');
} catch (e) {
if (e is GrpcError) {
print('gRPC Error: ${e.message} (Code: ${e.code})');
} else {
print('Unexpected Error: $e');
}
}
```
gRPC interceptors allow you to intercept and manipulate RPC calls at the client or server side. This can be used for logging, authentication, error handling, and more.
```dart
class ExampleInterceptor extends ClientInterceptor {
@override
ResponseFuture<R> interceptUnary<Q, R>(
ClientMethod<Q, R> method, ServiceCall call, Q request, CallOptions options, ClientUnaryInvoker<Q, R> invoker) {
print('Intercepting request: $request');
return invoker(method, call, request, options);
}
}
final channel = ClientChannel(
'localhost',
port: 50051,
options: const ChannelOptions(credentials: ChannelCredentials.insecure()),
interceptors: [ExampleInterceptor()],
);
```
Auth Interceptor example:
class AuthInterceptor extends ClientInterceptor {
final String token;
AuthInterceptor(this.token);
@override
ResponseFuture<R> interceptUnary<Q, R>(
ClientMethod<Q, R> method, ServiceCall call, Q request, CallOptions options, ClientUnaryInvoker<Q, R> invoker) {
final metadata = {
'authorization': 'Bearer $token',
};
final newCall = call.change(metadata: metadata);
return invoker(method, newCall, request, options);
}
}
final channel = ClientChannel(
'localhost',
port: 50051,
options: const ChannelOptions(credentials: ChannelCredentials.insecure()),
interceptors: [AuthInterceptor('your_token')],
);
examples of gRPC interceptors can be found in the gRPC Dart documentation.
gRPC middleware provides a way to add custom logic to gRPC services, such as logging, tracing, and monitoring. Middleware can be applied to individual methods or the entire service.
gRPC supports bidirectional streaming, enabling real-time communication between client and server. This can be used for chat applications, live data feeds, and other scenarios requiring continuous data exchange.
To optimize gRPC performance, consider using features such as connection pooling, compression, and caching. These can help reduce latency and improve overall system efficiency.
Use tools like grpc_cli for testing gRPC services, and debuggers like Dart DevTools for debugging Dart gRPC applications. These tools can help identify and resolve issues during development and testing.