Medium
Companies
Given an array of integers nums containing n + 1 integers where each integer is in the range [1, n] inclusive.
There is only one repeated number in nums, return this repeated number.
You must solve the problem without modifying the array nums and uses only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,4,2,2]
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,1,3,4,2]
Output: 3
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 105nums.length == n + 11 <= nums[i] <= n- All the integers in
numsappear only once except for precisely one integer which appears two or more times.
Follow up:
- How can we prove that at least one duplicate number must exist in
nums? - Can you solve the problem in linear runtime complexity?
-
Time complexity: O(n^2)
-
Space complexity: O(1)
// Brute Force Approach
// Time complexity --> O(n^2) and Space --> O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(nums[i]==nums[j])
{
return nums[i];
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
Note --
Above Code is not ❌ working due to time limit exceeded.
This is because above code has time complexity --> O(n^2). But it is also one of the approach to solve a problem
-
Time complexity: O(nlogn)
-
Space complexity: O(1)
// Using Sorting technique -- [Naive Approach]
// Time complexity --> O(nlogn) and Space --> O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(nums[i]==nums[i+1])
{
return nums[i];
}
}
return -1;
}
};
-
Time complexity: O(n)
-
Space complexity: O(n)
// Using Hashing Approach
// Time complexity --> O(n) and Space --> O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
map<int,int> mp;
for(auto it: nums)
{
mp[it]++;
}
for(auto i: mp)
{
if(i.second>1)
{
return i.first;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
-
Time complexity: O(n)
-
Space complexity: O(1)
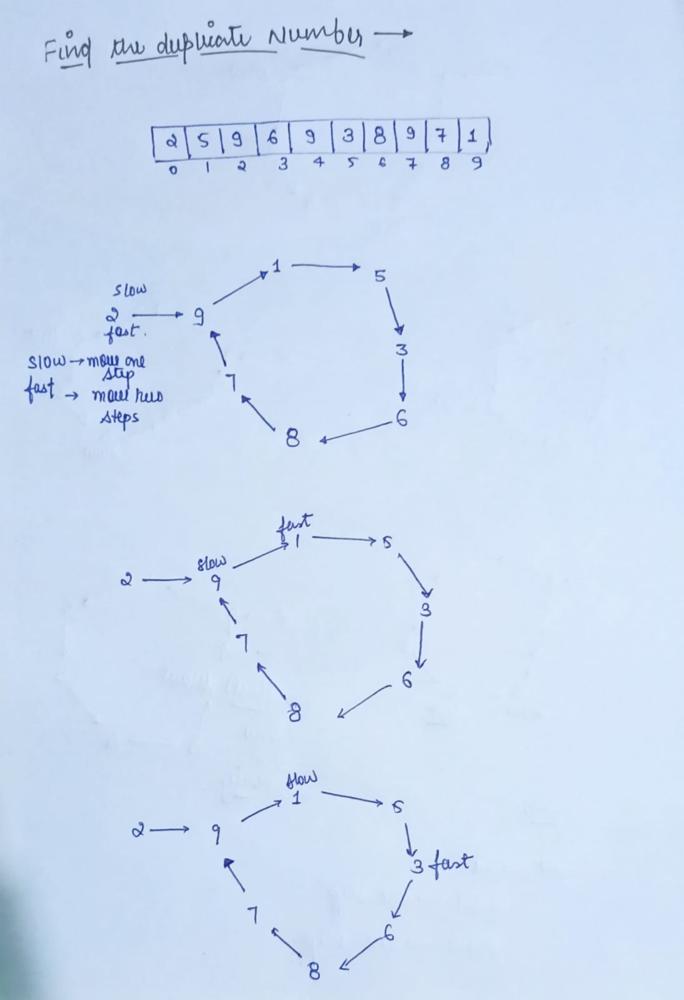
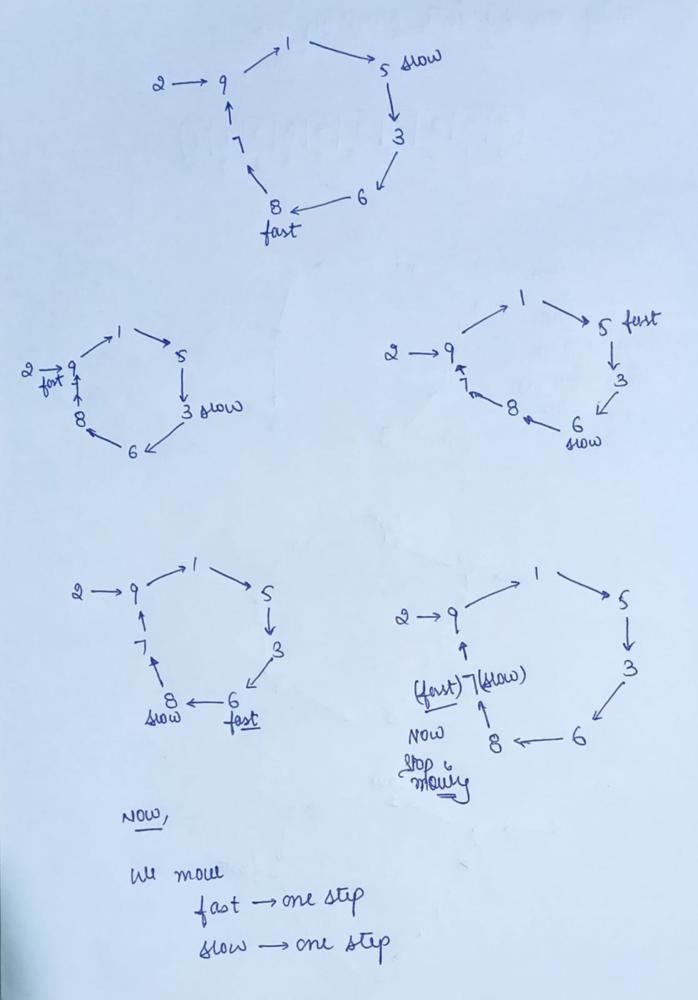
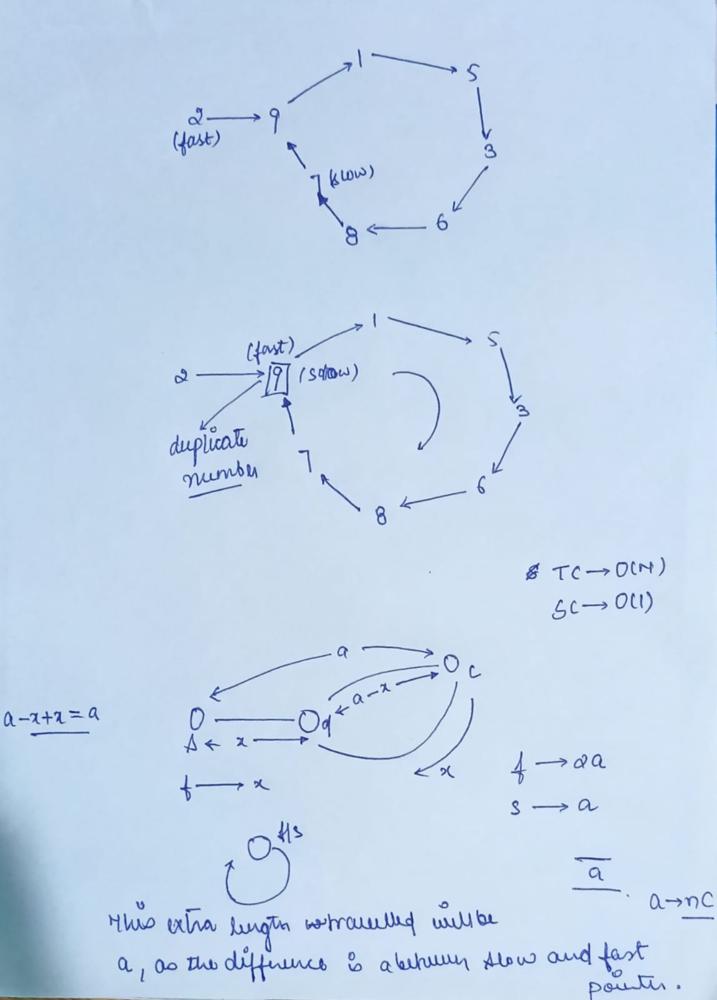
// Optimized Approach [Linked List Cyclic Method]
// Time complexity --> O(n) and Space --> O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
int slow=nums[0];
int fast=nums[0];
do{
slow=nums[slow]; // slow move one step
fast=nums[nums[fast]]; // fast move two step
}while(slow!=fast);
fast=nums[0];
while(slow!=fast)
{
// Now slow and fast both move one step
slow=nums[slow];
fast=nums[fast];
}
return slow;
}
};
Important Link