-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Usage and parameters
By default, the pipeline looks for FastQ ending in .fastq.gz files in the current directory. Paired or single-end data are handled transparently if your paired data are tag with the R1/R2 strings (see later).
cd data_directory_with_fastq_files
sequana_fastqc
This step prepares the pipeline. If everything went well, you should see something like that:
INFO [sequana.pipelines_common]: Welcome to Sequana pipelines suite (sequana.readthedocs.io)
INFO [sequana.pipelines_common]: Found 12 files matching your input pattern (*fastq.gz)
INFO [sequana.pipelines_common]: readtag: _R[12]_
INFO [sequana.pipelines_common]: Found 6 projects/samples
INFO [sequana.pipelines_common]: Your input data seems to be made of paired reads
Once ready execute the script fastqc.sh using
cd fastqc; sh fastqc.sh
Check that the information are correct and follow the instructions to execute the pipeline:
cd fastqc
sh fastqc.sh
If you do a local run, the last command will execute a snakemake pipeline locally. If you are on a SLURM cluster, the script fastqc.sh should already incorporate the slurm options and you just need to type:
cd fastqc
srun -c 1 sh fastqc.sh
# or sbatch -c 1 --wrap "sh fastqc.sh"
In both cases, once done, go to the output directory and open the summary.html file. If everything is fine, you can clean up the directory as follows:
make clean
In the summary.html file, you entry point looks like in the following image. From there you get a quick overview of the quality of the run. You can find links to individual fastqc report as well as a multiqc report:
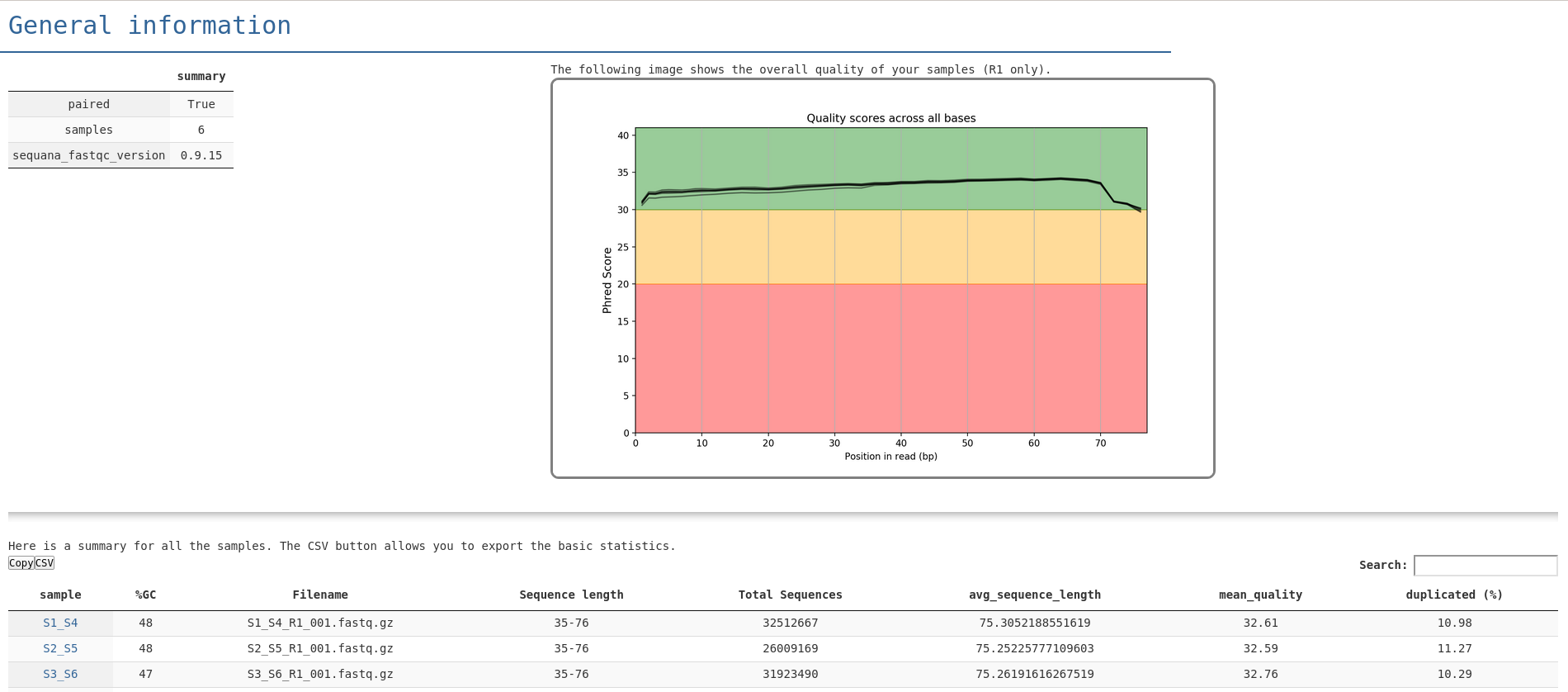
sequana_fastqc --input ~/data/project1 --output ~/my_fastqc/project1_qc
cd project1_qc
sh fastqc.sh
By default, if the sbatch command is found, the pipeline will consider that you are on a SLURM cluster and will set default options for you (e.g. memory of 4Gb). This will be super-seed by the pipeline requirements, which can be found in the file cluster_config.json
By default, locally we will use 4 jobs. On a cluster, we define the number of jobs to 40. If you wish to use more, just use the --jobs options when initialising the pipeline:
sequana_fastqc --jobs 100
Note that by default fastqc tool will use 4 cores per job. So here, you will be able to analyse 100 samples launching 100 fastqc, each of them asking for 4 cores.
This pipeline is part of the Sequana project. If you use sequana_demultiplex, please consider citing us. Visit the How to cite ? section. You may also visit the pipeline page and star us.