-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Merge pull request #207 from CabrilloRoboticsClub/docs
- Loading branch information
Showing
22 changed files
with
575 additions
and
369 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -1,279 +1,37 @@ | ||
| # Cabrillo ROV 2023 | ||
| <div align="center"><img src="doc/img/CRC_logo_orange.svg" width="400" alt="CRC Logo"></div> | ||
|
|
||
| ## SeaHawk II | ||
| SeaHawk is a project designed by a team of community college students from [Cabrillo College](https://www.cabrillo.edu/) in Aptos, California. Our latest project, SeaHawk II continues Cabrillo Robotics legacy of [SeaHawk I](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/releases/tag/MATEROV-2023) and [Hydrozoa](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2022) and will compete in the 2024 [MATE](https://materovcompetition.org/world-championship) International Competition. MATE challenges teams worldwide to build a Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) that can complete simulated real-world tasks underwater. Teams also demonstrate their robot's functionality and design rationale through marketing, documentation, a presentation, and more. Previously, Cabrillo Robotics has competed in the Pioneer division of the competition and took home first place the last two consecutive years. This year, we take on the challenge of developing a ROV to compete in the highest class of the competition: Explore. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Getting started developing | ||
| Are you new here? If so, welcome to Cabrillo Robotics Club! To get started developing for this project, the following documents will be useful. | ||
|
|
||
| | Documentation content | File | | ||
| | ---- | ---- | | ||
| | Getting started developing | [getting_started.md](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/getting_started.md) | | ||
| | Running the project | [run.md](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/run.md) | | ||
|
|
||
| The additional resources below may also be of assistance. | ||
| | Resource | Link | | ||
| | ---- | ---- | | ||
| | ROS2 Humble documentation | [ROS 2 Documentation: Humble Hawksbill](https://docs.ros.org/en/humble/index.html) | ||
| | Software team onboarding repo | [TinyHawk GitHub](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/tiny_hawk) | ||
| | Software team onboarding videos | [TinyHawk YouTube Playlist](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hzFErKeImTs&list=PLrhUbqBwgd2hjlbSZ6VrAEFjsnTWKxhTc) | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Documentation | ||
| Documentation for the software in this repo is found in the [`doc`](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/tree/main/doc) directory. | ||
|
|
||
| | Documentation content | File | | ||
| | ---- | ---- | | ||
| | Project architecture | [architecture.md ](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/architecture.md) | | ||
| | Notes on the cameras| [camera_notes.md ](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/camera_notes.md) | | ||
| | Getting started developing | [getting_started.md](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/getting_started.md) | | ||
| | Using Git/GitHub | [github.md ](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/github.md) | | ||
| | ROS parameters and the SetRemoteParams class| [params.md](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/params.md) | | ||
| | Using and updating RViz | [rviz.md](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/rviz.md) | | ||
| | Running the project | [run.md](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/run.md) | | ||
| | Collecting and running ROS bags | [ros_bags.md](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/ros_bags.md) | | ||
| | Miscellaneous notes on the ROS packaging process | [rosdep_notes.md](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/rosdep_notes.md) | | ||
| | Project style guide (Python) | [style_guide_python.md](https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023/blob/main/doc/style_guide_python.md) | | ||
|
|
||
| Cabrillo College Robotics Club repo for the MATE ROV 2023 competition. This README file has information to get you started developing the robot. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Setup GitHub | ||
|
|
||
| In order to use this repository you should have generated SSH keys and uploaded your public key to GitHub. If you have not yet created an SSH key on your machine do the following. **Skip these steps if you have an SSH key in GitHub already**. | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Create an SSH key if you don't have one already. | ||
| ```console | ||
| ssh-keygen -t ed25519 | ||
| ``` | ||
| Use the default location, set a password if you like. | ||
| 1. Copy and paste your public key into GitHub | ||
| ```console | ||
| cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub | ||
| ``` | ||
| Full instructions for how to add a public key to GitHub can be found in [GitHub's official documentation](https://docs.github.com/en/authentication/connecting-to-github-with-ssh/adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-github-account#adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-account). | ||
|
|
||
| ## Checkout the Code | ||
|
|
||
| **These instructions are for Mac, Windows and Linux.** On Windows you should use PowerShell, not the old command line. | ||
|
|
||
| To get the code in this repository on your computer, dev box or RPi you should run the following commands. These commands assume that you have setup your SSH keys in GitHub according to the instructions in the "Setup GitHub" section above. | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Check if you have `git` installed on your computer. | ||
| ```console | ||
| git --version | ||
| ``` | ||
| **If you don't have Git installed:** | ||
| 1. Install Git on your platform by following the official [GIT Getting Started Instructions](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Getting-Started-Installing-Git). | ||
| 1. Setup `git` by entering in your name and email address. The email address should be the one you have registered with GitHub. | ||
| ```console | ||
| git config --global user.name "Your Name" | ||
| git config --global user.email "you@you.com" | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Check out this repository into your home directory. | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| cd | ||
| git clone git@github.com:CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023.git | ||
| cd ~/cabrillo_rov_2023 | ||
| git submodule init | ||
| git submodule update | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Now you have the source code on your computer and you should be able to make new branches and your own changes. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Getting Started (Mac and Windows Setup) | ||
|
|
||
| If you have a Windows or Mac desktop (or Linux that's not Ubuntu 22.04) you can use Docker and Development Containers in vscode to do local development. This is the fastest and easiest way to get setup and eables you to run and test nodes on your computer. That's good for learning but you won't be able to use the ROS2 network or use devices like a joystick or camera. | ||
|
|
||
| 1. [Install vscode](https://code.visualstudio.com/) | ||
| 1. [Install Docker Desktop](https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop/) | ||
| 1. Follow the [Dev Containers Tutorial](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/devcontainers/tutorial) | ||
| 1. In vscode open the `cabrillo_rov_2023` directory that you checked out using the "Checkout the Code" procedure above with the `File -> Open Folder` menu. Vscode will prompt you to create a dev container. Follow the prompts. Building the container could take 10 to 20 minutes but you only have to do it once. | ||
| 1. Create a Terminal in your vscode window with the `Terminal -> New Terminal` menu. | ||
| 1. Build the software in your dev container: | ||
|
|
||
| **Run this command in the dev container terminal.** | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| make | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Alternatively, if you don't want to use the container inside of VSCode, you can run | ||
| ```console | ||
| docker build -t ros2-container:<tag> .devcontainer | ||
| docker run --user vscode -v .:/home/vscode/cabrillo_rov_2023 --network host -it ros2-container:<tag> | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Ubuntu 22.04 Desktop Setup | ||
|
|
||
| If you have Ubuntu 22.04 on your desktop you don't need a dev container because you can run everything natively. Only Ubuntu machines will be able to use hardware and communicate with other machines in the ROS2 network. These instructions assume you have already cloned the repository by following the "Checkout the Code" procedure above. | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Install the necessary software packages | ||
| ```console | ||
| sudo apt update -y && sudo apt install -y git ansible python3-pip vim | ||
| ``` | ||
| 1. Use `make` to install ROS2 and all the necessary packages. | ||
| ```console | ||
| make devbox-install | ||
| ``` | ||
| **This will take a while!** | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Put ROS on your path | ||
| ```console | ||
| echo 'if [ -z "$ROS_DISTRO" ]; then source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash; fi' >> ~/.bashrc | ||
| ``` | ||
| 1. **Start a new shell** and build the repository | ||
| ```console | ||
| make | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| You Desktop is now a dev box. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Raspberry Pi 4 Setup | ||
|
|
||
| Start by creating a bootable SD card image: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. On your local computer download and install [Raspberry Pi Imager](https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/) | ||
| 1. Attach a Micro SD card to your local computer | ||
| 1. Open Raspberry Pi Imager | ||
| * `CHOOSE OS` > `Other general-purpose OS` > `Ubuntu` > `Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS (64-bit)` | ||
| * Choose the Micro SD card as the storage and hit `WRITE` | ||
| 1. Unplug the Micro SD card from your local computer, plug it back in to your local computer. | ||
| 1. Copy the `user-data` file from `setup/image` into the `system-boot` volume that shows up (overwrite the existing file). | ||
| 1. Install the SD card into the Raspberry Pi | ||
| 1. Connect the Pi to an ethernet connection with internet access | ||
| 1. Plug the power cable in to the Pi. | ||
|
|
||
| The Pi will boot, then reboot. Give it 10 minutes or so. The hostname and passwords are now set. SSH is enabled. You can connect with: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| ssh -A ubuntu@seahawk.local | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Once you have SSHed into the new Pi image run the ROV specific playbooks: | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Check out this repository into your home directory. | ||
| ```console | ||
| cd | ||
| git clone https://github.com/CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023.git | ||
| cd ~/cabrillo_rov_2023 | ||
| git submodule init | ||
| git submodule update | ||
| ``` | ||
| 1. Install make and Ansible command | ||
| ```console | ||
| sudo apt install make ansible | ||
| ``` | ||
| 1. Use `make` to install ROS2 and all the necessary packages. | ||
| ```console | ||
| make rov-install | ||
| ``` | ||
| **This could take a long, long time!** up to 30 minutes. | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Reboot the Pi | ||
| ```console | ||
| sudo reboot | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| The `make rov-install` command installs ROS2 and creates user accounts on the Raspberry Pi. After rebooting you should be able to login with your own username. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Using vscode to Connect to a Pi | ||
|
|
||
| The best way to access the Raspberry Pi for software development is using vscode. You can use the access to develop and test nodes that run on the Pi or to just start the ROV during development of deck nodes. Assuming you have your own computer setup per the instructions above, perform the following steps to access the Pi. | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Install the [Remote SSH plugin](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/remote/remote-overview) into vscode | ||
| 1. Click the remote status bar on the very bottom left of the window. (You can find some tips in the [Remote SSH tutorial](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/remote/ssh-tutorial).) | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| The Remote Status bar item can quickly show you in which context VS Code is running (local or remote) and clicking on the item will bring up the Remote - SSH commands. | ||
|
|
||
| 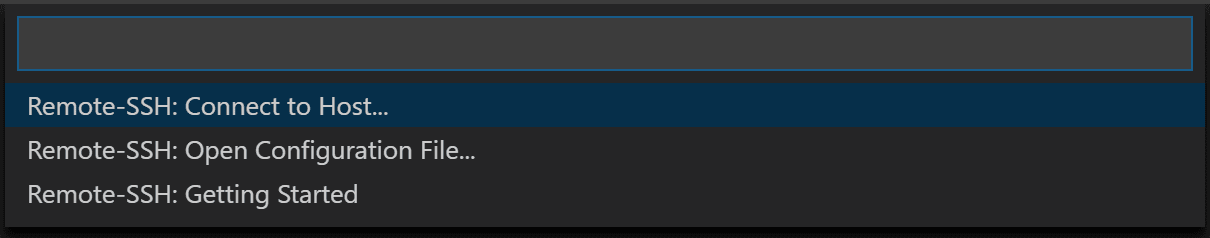 | ||
| 1. Type the ssh command into the top bar: | ||
|
|
||
| 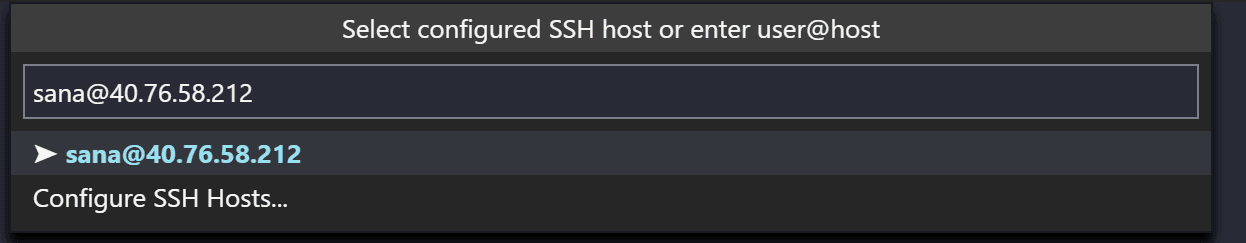 | ||
|
|
||
| > The command will look like: **ssh yourname@seachicken.local -A** | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Follow the prompts: | ||
| 1. Choose the first option for where to save the configuration. | ||
| 1. Choose "Linux" type if asked. | ||
| 1. Choose "Yes" if this is your first time connecting to this Pi. | ||
|
|
||
| 1. You should see that you are connected: | ||
|
|
||
| 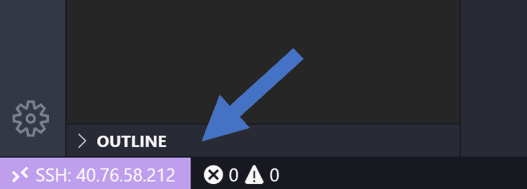 | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Now that you're connected, start a new Terminal using the `Terminal -> New Terminal` menu. | ||
| 1. Create a copy of the repo in your home directory: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| cd | ||
| git clone git@github.com:CabrilloRoboticsClub/cabrillo_rov_2023.git | ||
| cd ~/cabrillo_rov_2023 | ||
| git submodule init | ||
| git submodule update | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Configure git on the Pi4: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| git config --global user.name "Your Name" | ||
| git config --global user.email "you@you.com" | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Add ROS to your startup scripts: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| echo 'if [ -z "$ROS_DISTRO" ]; then source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash; fi' >> ~/.bashrc | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Exit your current terminal and start a new one. | ||
| 1. Build the ROS project | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| cd ~/cabrillo_rov_2023 | ||
| make | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Vscode will remember everything for next time. You should only have to do this once. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Building the Nodes | ||
|
|
||
| The ROS nodes are built with the `colcon` program. A `makefile` is present to help me remember what the `colcon` commands are. Build the project with: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| make | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| The build artifacts are in: | ||
|
|
||
| - `build` | ||
| - `install` | ||
| - `log` | ||
|
|
||
| Clean the build with: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| make clean | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Starting the ROV and Deck ROS2 Nodes | ||
|
|
||
| The easiest way to launch is by `make`. To launch the deck nodes and RQT viewer run: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| $ make deck | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| To launch all the nodes on the ROV run: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| $ make rov | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Launch Files | ||
|
|
||
| We've migrated all the launch files to their respective ROS packages. To use the launch files you must first run the `install/local_setup.XXX` script. | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| ros2 launch seahawk rov.launch.py | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| To launch all the nodes on the deck: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| ros2 launch seahawk deck.launch.py | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Running Individual Nodes | ||
|
|
||
| The built nodes are a part of a local build area. Source the following script to setup your paths: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| source install/setup.bash # Choose one that matches your shell. | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Run the Python examples: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| ros2 run seahawk example_pub | ||
| ros2 run seahawk example_sub | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## Launching the Kinematics Debug Nodes | ||
|
|
||
| Do this to launch the debug nodes. It also starts RViz: | ||
|
|
||
| ```console | ||
| $ ros2 launch seahawk kinematics_viz.launch.py | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| You have to separately launch the other deck nodes. |
File renamed without changes.
Oops, something went wrong.