Pytorch Implementation of paper:
Robust and Accurate Hand Gesture Authentication With Cross-Modality Local-Global Behavior Analysis
Yufeng Zhang, Wenxiong Kang*, and Wenwei Song.
Obtaining robust fine-grained behavioral features is critical for dynamic hand gesture authentication. However, behavioral characteristics are abstract and complex, making them more difficult to capture than physiological characteristics. Moreover, various illumination and backgrounds in practical applications pose additional challenges to existing methods because commonly used RGB videos are sensitive to them. To overcome this robustness limitation, we propose a two-stream CNN-based cross-modality local-global network (CMLG-Net) with two complementary modules to enhance the discriminability and robustness of behavioral features. First, we introduce a temporal scale pyramid (TSP) module consisting of multiple parallel convolution subbranches with different temporal kernel sizes to capture the fine-grained local motion cues at various temporal scales. Second, a cross-modality temporal non-local (CMTNL) module is devised to simultaneously aggregate the global temporal features and cross-modality features with an attention mechanism. Through the complementary combination of the TSP and CMTNL modules, our CMLG-Net obtains a comprehensive and robust behavioral representation that contains both multi-scale (short- and long-term) and multimodal (RGB-D) behavioral information. Extensive experiments are conducted on the largest dataset, SCUT-DHGA, and a simulated practical dataset, SCUT-DHGA-br, to demonstrate the effectiveness of CMLG-Net in exploiting fine-grained behavioral features and complementary multimodal information. Finally, it achieves stat-of-the-art performance with the lowest ERR of 0.497% and 4.848% in two challenging evaluation protocols and shows significant superiority in robustness under practical scenes with unsatisfactory illumination and backgrounds.
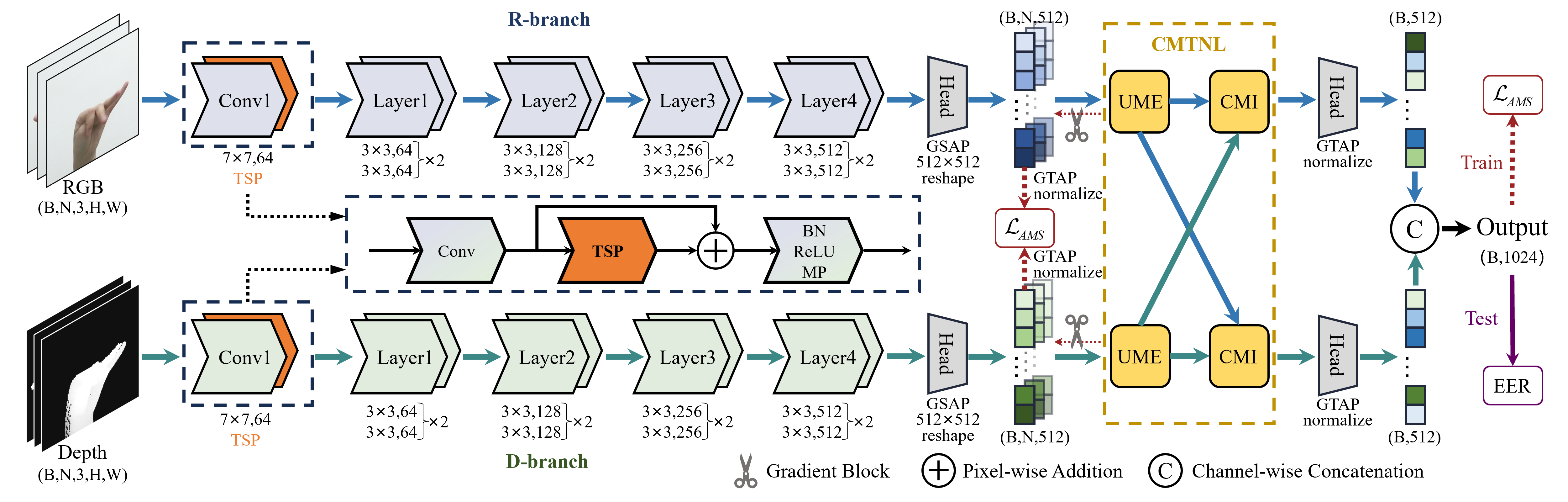
The overall architecture of the CMLG-Net. It contains two independent branches (R- and D-branches) for RGB and depth data analysis. In each branch, we utilize the pretrained ResNet18 as the backbone and insert a TSP module at the Conv1 block with a residual connection to extract local motion cues. At the end of the two branches, the CMTNL module is proposed to summarize the global temporal and multimodal information using the UME and CMI modules. Finally, enhanced features from the R- and D-branches are concatenated to generate the final identity feature. In the training stage, the unimodal identity features from the R- and D-branches, and the final multimodal identity feature are supervised by three independent loss functions. Meanwhile, the gradient from the CMTNL module is blocked in back-propagation, thus the R- and D-branches could focus on extracting modality-specific features without interference from the other modality. The MP, GSAP, and GTAP denote max pooling, global spatial average pooling, and global temporal average pooling, respectively.
The SCUT-DHGA dataset is collected indoors with an ideal illumination and pure background, which is different from practical scenes. To evaluate the robustness of the model in application scenarios, we performed background replacement and lighting adjustment to the testing set of the original SCUT-DHGA dataset, resulting in a challenging derived SCUT-DHGA-br dataset that is closer to real-world scenarios. The backgrounds, with a total number of 3627, are collected from the internet and the real world, covering airports, classrooms, malls, museums, subways, etc. The lighting condition of the hand area is controlled by a random brightness factor ranging from 0.5 to 1.
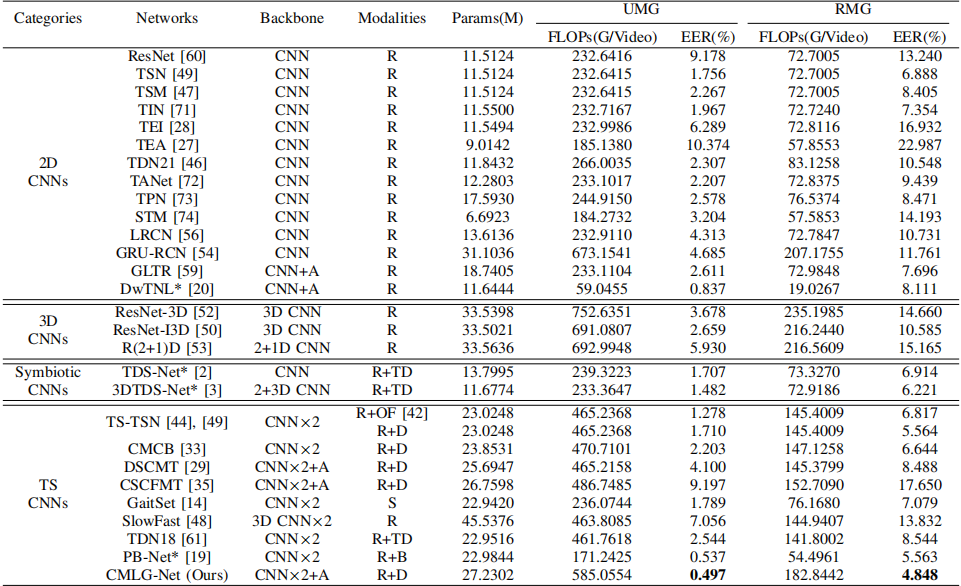
To prove the rationality and superiority of our CMLG-Net, we conduct extensive experiments on the SCUT-DHGA and SCUT-DHGA-br datasets. The EERs shown in the following two tables are all average values over six test configurations on the cross session.
EER performance on the SCUT-DHGA dataset. We compare the proposed CMLG-Net with 27 state-of-the-art methods including 2D CNNs, 3D CNNs, symbiotic CNNs, and TS CNNs. The CMLG-Net achieve both best EER performance under UMG and RMG protocols, demonstrating its superior accuracy.
EER and efficiency performance on the SCUT-DHGA-br dataset. Efficiency is also a critical criterion for authentication algorithms since real-time response with low latency is decisive to user experience in practical applications. Thus, we present the EERs and FLOPs of each model under UMG (64 frames per video) and RMG (20 frames per video) protocols. Our CMLG-Net achieves the lowest EER (4.144 % for UMG, 9.669 % for RMG) and significantly outperforms other approaches. In erms of efficiency, it can meet the real-time requirements on the GPU devices.
Please make sure the following libraries are installed successfully:
- PyTorch >= 2.2.1
This repository is a demo of CMLG-Net. Through debugging (main.py), you can quickly understand the configuration and building method of CMLG-Net.
If you want to explore the entire dynamic hand gesture authentication framework, please refer to our pervious work SCUT-DHGA or send an email to Prof. Kang (auwxkang@scut.edu.cn).